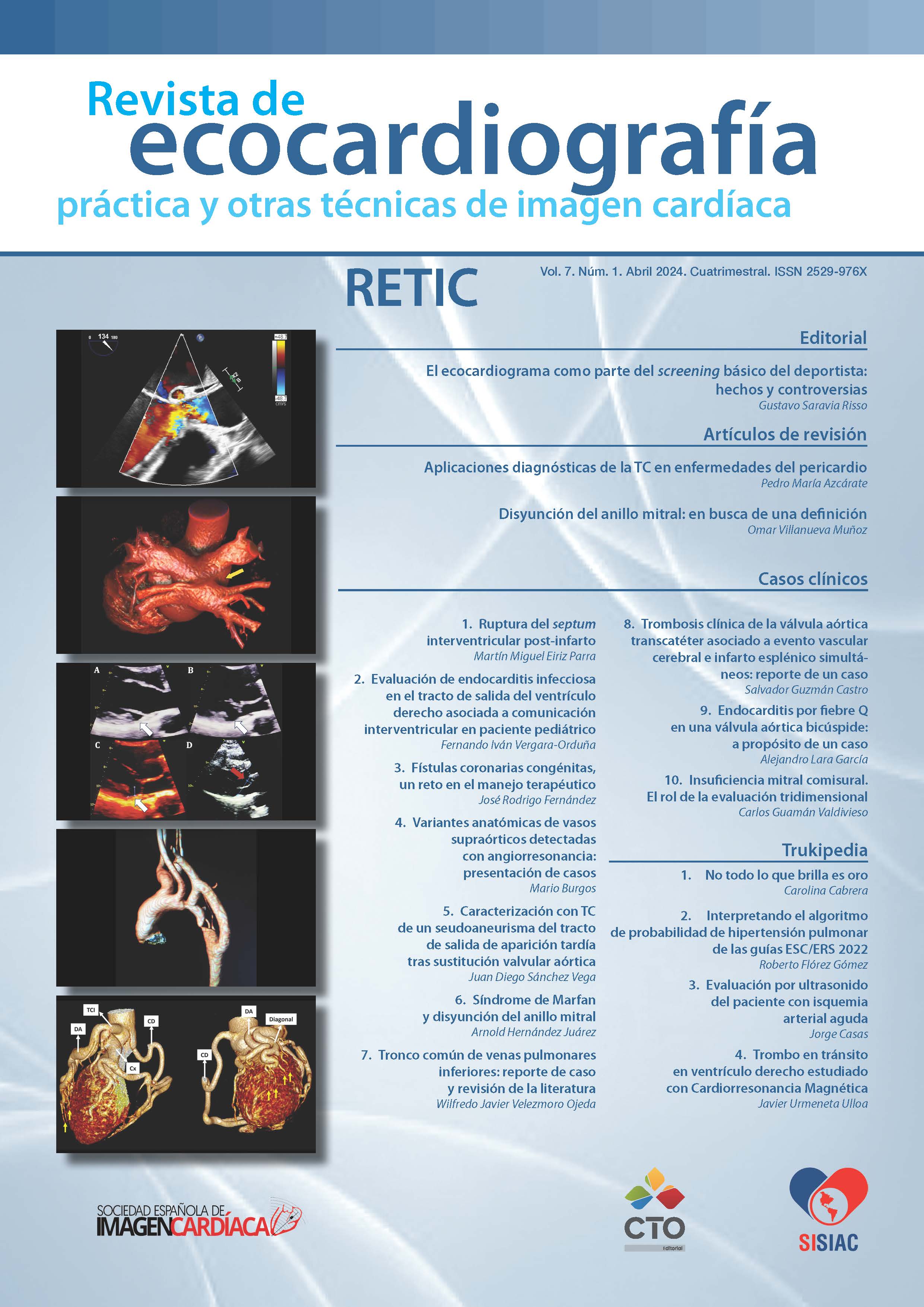
Post-infarction interventricular septum rupture
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37615/retic.v7n1a4Keywords:
interventricular communication, septum rupture, advanced myocardial infarctionAbstract
With the beginning of reperfusion, especially with percutaneous coronary intervention, the mortality and the incidence of mechanical complications from acute myocardial infarction have decreased considerably. The time from the onset of symptoms to reperfusion is a fundamental factor; any delay favors the appearance of rupture of the free wall of left ventricle, interventricular septum, or papillary muscle. Currently, rupture of the interventricular septum is a rare but devastating complication that, despite timely medical and surgical treatment, presents high mortality.
Downloads
Metrics
References
Puerto E, Viana-Tejedor A, Martínez-Sellés M, Domínguez-Pérez L, Moreno G, Martín-Asenjo R, et al. Temporal Trends in Mechanical Complications of Acute Myocardial Infarction in the Elderly. Journal of the American
College of Cardiology 2018;72(9):959-66. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2018.06.031 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2018.06.031
Crenshaw BS, Granger CB, Birnbaum Y, Pieper KS, Morris DC, Kleiman NS, et al. Risk Factors, Angiographic Patterns, and Outcomes in Patients with Ventricular Septal Defect Complicating Acute Myocardial Infarction. Circulation.2000;101(1):27-32. doi: https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.101.1.27 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.101.1.27
Magalhães P, Mateus P, Carvalho S, Leão S, Cordeiro F, Moreira JI, et al. Relationship between treatment delay and type of reperfusion therapy and mechanical complications of acute myocardial infarction. European HeartJournal: Acute Cardiovascular Care 2016; 5(5):468-74. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/2048872616637038 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/2048872616637038
Bajaj A, Sethi A, Rathor P, Suppogu N, Sethi A. Acute Complications of Myocardial Infarction in the Current Era: Diagnosis and Management. Journal of Investigative Medicine 2015. 63(7):844-55. doi:https://doi.org/10.1097/JIM.0000000000000232 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/JIM.0000000000000232
Hamilton MCK, Rodrigues JCL, Martin RP, Manghat NE, Turner MS. The In Vivo Morphology of Post-Infarct Ventricular Septal Defect and the Implications for Closure. JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions 2017;10(12):1233-43.doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcin.2017.03.042 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcin.2017.03.042
Villaescusa JM, Otero JJ, Mataró MJ, Porras C, Melero JM. Comunicación interventricular postinfarto visualizada mediante tomografía computarizada. Revisión del diagnóstico. Cirugía Cardiovascular 2020; 27(4):148-50. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.circv.2020.01.004 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.circv.2020.01.004
Sutton MGStJ, Sharpe N. Left Ventricular Remodeling After Myocardial Infarction: Pathophysiology and Therapy. Circulation 2000;101(25):2981-8. doi: https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.101.25.2981 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.101.25.2981
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Martín Miguel Eiriz Parra, Emilio Arbas Redondo

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
RETIC is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) license https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0 which allows sharing, copying and redistribution of the material in any medium or format, under the following terms:
- Attribution: you must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests that the licensor endorses you or your use.
- Non-commercial: you may not use the material for commercial purposes.
- No Derivatives: if you remix, transform or build upon the material, you may not distribute the modified material.
- No Additional Restrictions: you may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything permitted by the license.